SNMP Discovery
3 minute read
Introduction
The goal with Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) discovery is to identify and classify all SNMP-enabled network devices and make them available as a typed device in the discovery. SNMP-enabled network devices are, for example, routers, switches, printers or firewalls. The term “identify” is used here to refer to the process of determining all active network devices and checking them for SNMP capability. During classification, devices are assigned according to their intended use. For example, switches, routers and firewalls are necessary to form a network. A printer or an SNMP-enabled IoT device, on the other hand, are participants in a network. As part of the typing process, the exact type of network device is determined so that the exact information that is relevant to that device type is captured. For example, consumables are recorded for printers, and the individual network ports are recorded for switches.
The biggest challenge in discovery is the classification and typing of SNMP-enabled network devices, as the SNMP protocol does not provide information about the device class and type. Through years of experience and support of Docusnap users, we are able to identify and record a variety of device types according to the purpose of use.
Discovery
Currently, there are three basic SNMP versions. SNMPv1, SNMPv2 and SNMPv3: SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not use encryption algorithms to transmit data. SNMPv3, on the other hand, supports security solutions such as user accounts, authentication, or encryption. Because of these differences, Docusnap365 has SNMPv1/-v2 and SNMPv3 wizards for discovery.
The possible and valid notations for IP address, IP address ranges and hostname can be found in the Wizard manual.
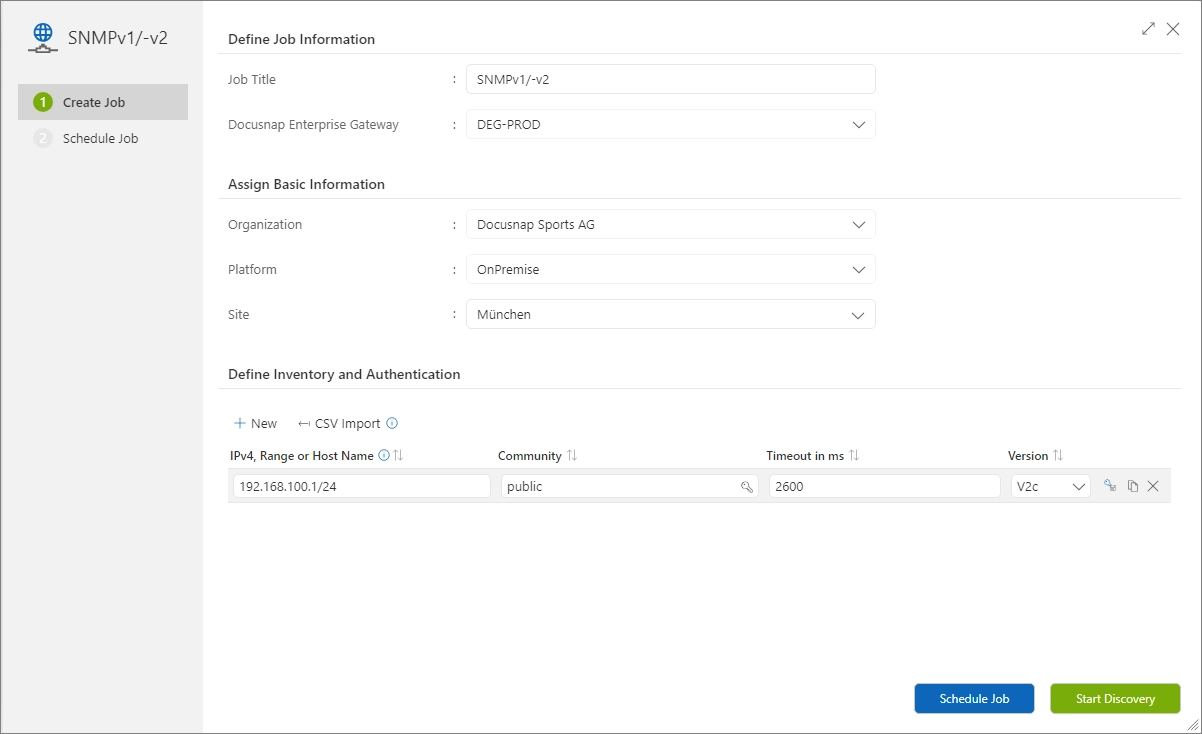
“SNMPv1/-v2” Wizard
SNMPv2 exists in the versions SNMPv2c, -v2p and v2u. SNMPv2c (community-based SNMP) is by far the most widespread SNMP version, which is also supported by Docusnap365. The GetBulk method is used to query device information. SNMPv1 only uses the GetNext method. Older devices that only support SNMPv1 can also be inventoried with the version “V1” option.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use a string called the “community string” for authentication. Most manufacturers preassign the “Community String” with the character string “public”, which allows read access to the devices. In the meantime, it is common to enter a user-defined string here for security reasons. Accordingly, this string must be known for a successful discovery. If the SNMP discovery is to be carried out by scheduling, it is assumed that the login information is stored in the vault.
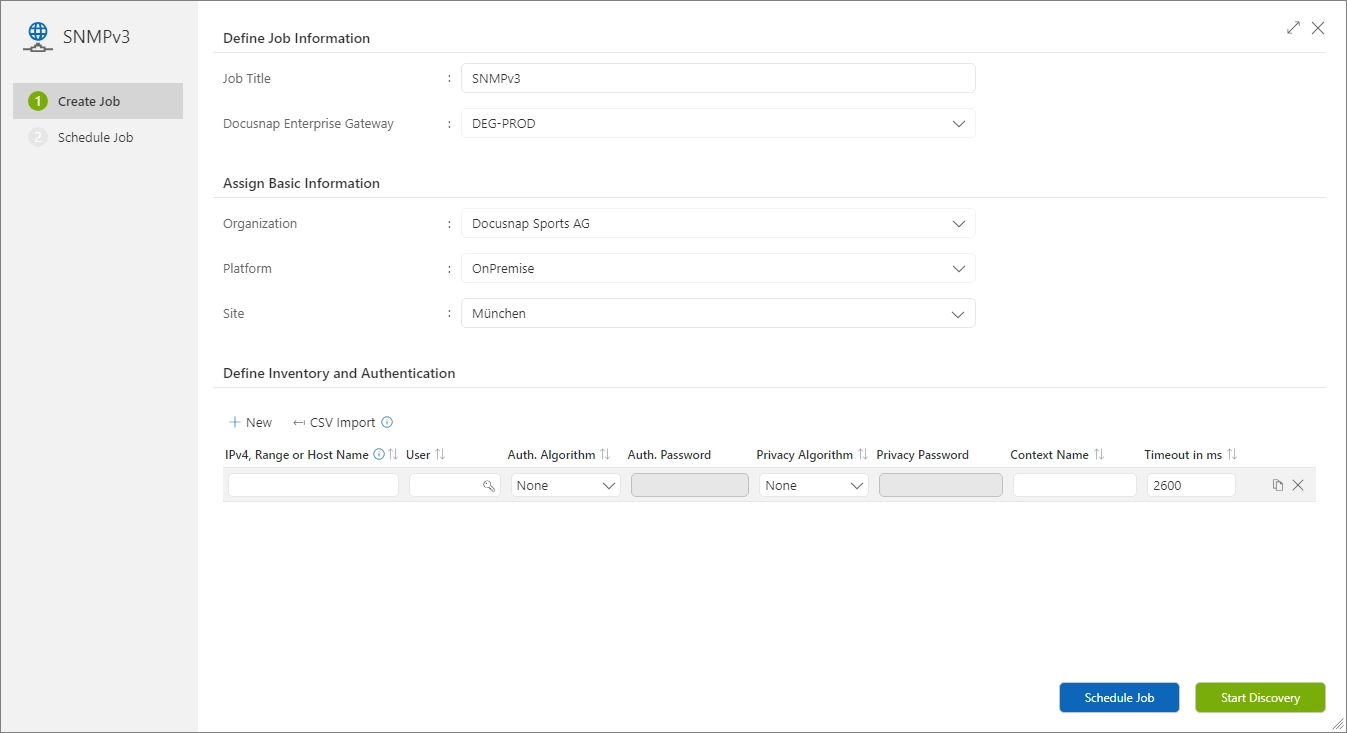
“SNMPv3” Wizard
SNMPv3 expects logon information to be transmitted in encrypted form when logging on. In the SNMPv3 wizard the properties User, Auth. Algorithm, Auth. Password, Private Algorithm, Private Password and Context Name are available.